ITSM lessons from Toyota principles
IT stakeholders constantly strive for cost reduction and resource optimization. DevOps, agile and lean methodologies are rapidly used in IT Service Management (ITSM) to drive efficiency. There is a paradigm shift in the way services are delivered today. IT has shifted from a fire-fighting function to a proactive customer-centric function. In this blog, let us discuss how Toyota lean principles inspire IT function to achieve value through waste reduction.
Lean principle is derived from Toyota Production System (TPS) to eliminate waste in car manufacturing. “It is an integrated socio-technical system and a management philosophy to eliminate waste and improve interaction between people & technology.” Eliminating waste involves identifying bottlenecks and it includes resources such as time, material and people. It is necessary to understand the type of waste and apply specific ways to eliminate it. Agile and DevOps methodologies are subsets of lean principles which maintain a balance between “Doing more” and “Doing too little”.
The Toyota Principle
Continual Improvement and Respect for People are two key considerations adopted by Toyota Sakichi Toyoda. There are fourteen guiding principles of Toyota that are divided into four broad categories as follows:
- Long Term Philosophy
- The right process will produce the right results
- Add value to the organization by developing your people and partners
- Continuously solving root problems drives organizational learning
How ‘Toyota way’ can drive an effective IT department
- Long Term Philosophy
- Communicate mission and vision of IT team to everyone
- Publish metrics to everyone across organization
- The right process will produce the right results
- Standardize ITSM processes to improve scalability
- Identify and implement only the necessary processes
- Eliminate unwanted approvals in CAB
- Add value to the organization by developing your people and partners
- Understand your IT agents and end users. Know their background, preferences and preferred channel to realize IT success
- Train your IT agents with diverse skills to be proactive
- Motivate your IT agents to push beyond boundaries to handle any critical incidents
- Continuously solving root problems drives organizational learning
- Solve the issue permanently rather than fire-fighting
- Prefer Problem analysis over temporary workaround
Objectives of lean IT
Lean IT is an extension of lean manufacturing principles to eliminate waste and improve value. The lean objectives are as follows: Breaking down complex processes; Reducing errors or defects; Cost reduction and Reduction in waiting time and lead time. There are three types of activities:
- Non value adding activities
- Necessary but non value adding
- Value adding activities
Identifying waste in ITSM
Some of the common examples for waste in ITSM processes include:
- Change request approvals that have longer waiting time and might act as a bottleneck
- Too many change rollbacks
- Unplanned downtime
- Knowledge base articles that are not easily discoverable by users to solve problems
- Frequently repeating incidents consume more resources affecting business productivity
- Ticket resolution dependency on other teams
- Ticket assigned to a wrong person
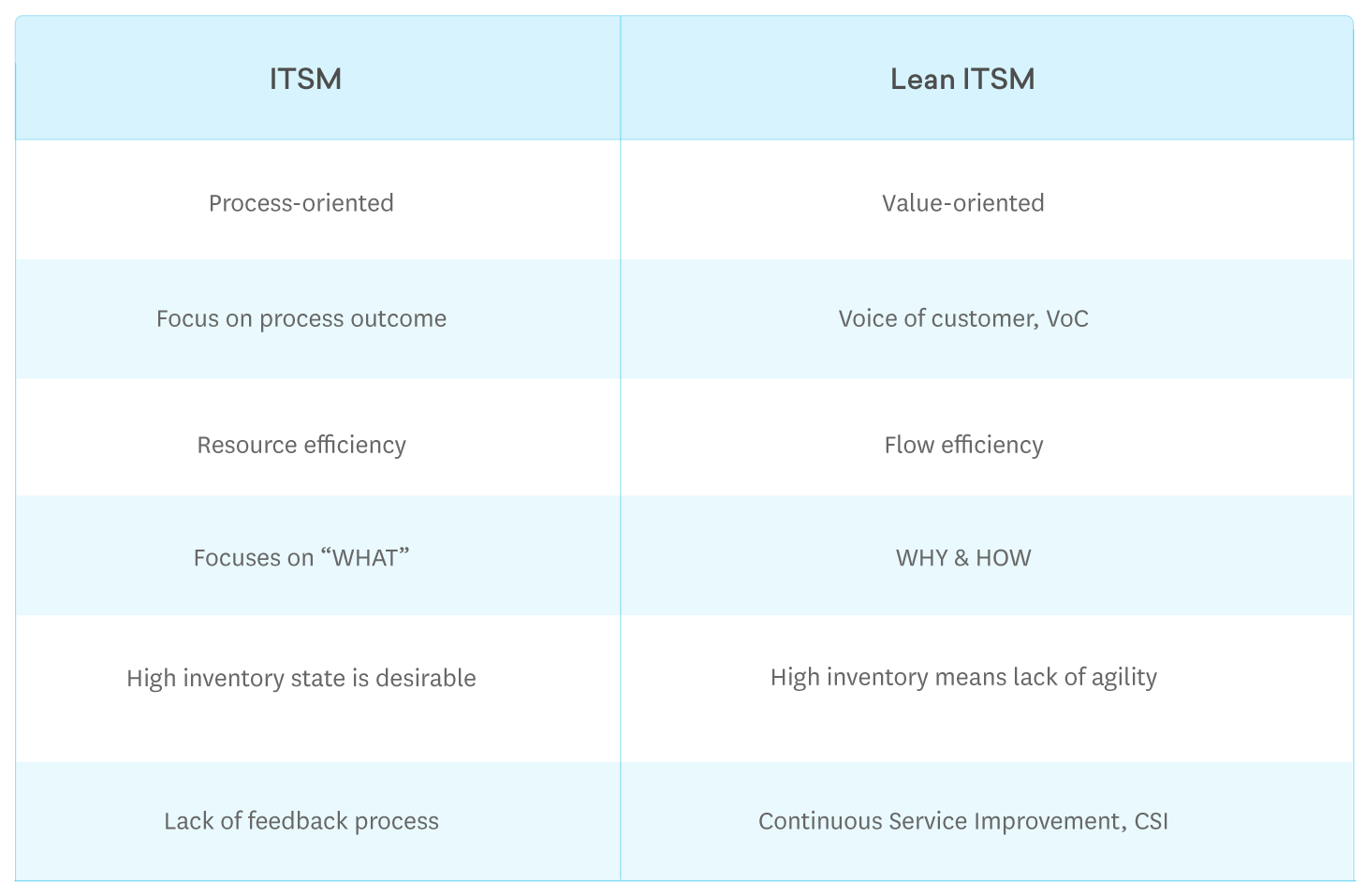
Differences – ITSM & Lean ITSM
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a lean technique to identify waste and remove them efficiently. This starts with visualizing activities and optimizing them by removing bottlenecks. The primary goal of value stream mapping technique is to improve customer value by eliminating non value adding bottlenecks.
Types of activities

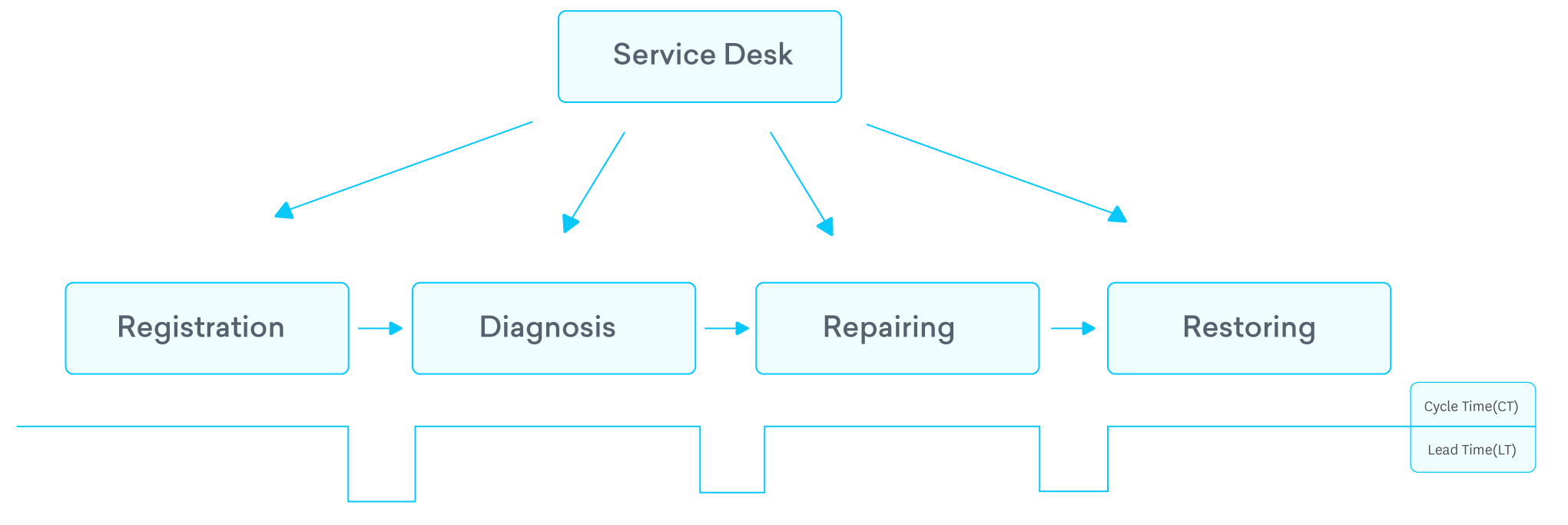
Incident value stream mapping – Implementation steps
- Identify stages of Incident process. Map only the essential stages of the process. For example, eliminate manual ticket classification, assignment and try to automate them
- Metrics – Record the time taken to complete each step and average waiting time between each step
- Visualize the process in a flow diagram understanding cycle time and waiting time
- Ensure waiting time between stages is not too high to become a constraint
- Identify the bottleneck and understand “why” and “how”
- Create an action plan to eliminate bottlenecks
Tip: Issue profiling is the first step and it is crucial to ensure whether it’s the right ticket type, assigned to the right person. There has to be an alignment between customer issue and service provider’s understanding of the issue. This saves a lot of time during investigation phase and provides faster resolution.
Summary
Toyota Principles teach a lot of lessons for ITSM. Process outcome can be improved largely by doing things slightly in a different way. Businesses benefit from Toyota lean philosophy in terms of cost reduction and resource optimization. Start with analysing your existing process and identify bottlenecks using the above method.
Discover more industry transformation stories that provide actionable insights and best-practices at the Freshworks Experience Roadshow; October 1st – 31st in 11 European capital cities. With talks and discussions on how to deliver modern IT services that match the scale of your business. Register for your tickets today.



